SCRIPTING
Scripting in RayStation provides automation, connectivity and flexibility beyond the standard user interface. Script languages IronPython and CPython give users access to all the operating system capabilities and applications such as file writing, process initiation, communication with other computers, and controlling scriptable applications such as Microsoft Office or .NET.
AUTOMATION
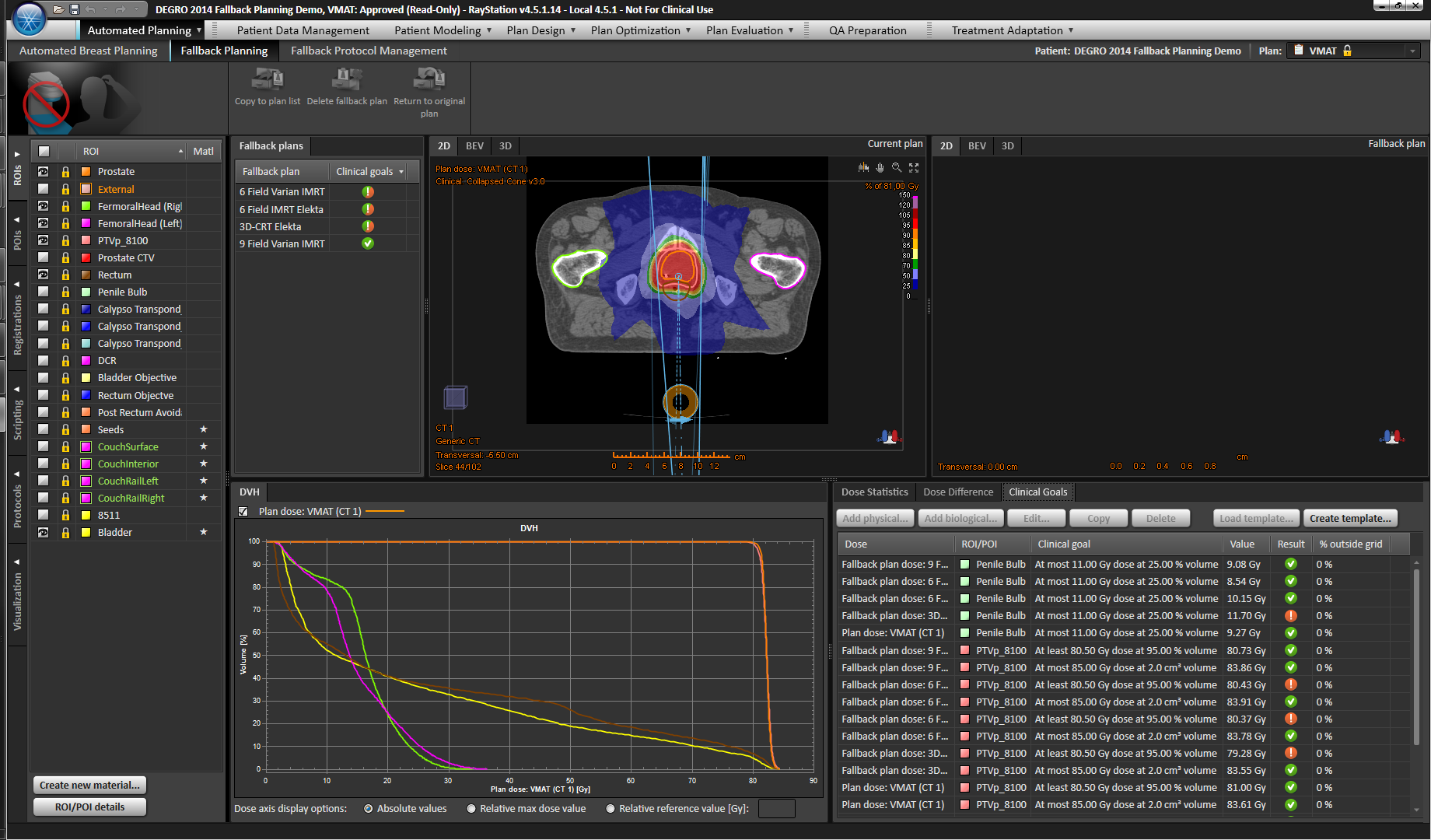
Clinic-specific procedures can be automated through scripting. Scripts can check for properties in a plan, such as small segments, disconnected target volumes, hotspots and undesirable gantry and couch angles. The system can then display a warning message or create a report.
CONNECTIVITY
Scripting provides a way to customize the interaction between RayStation and other systems for scenarios where DICOM is insufficient.
FLEXIBILITY
Scripting enables users to harness the power of RayStation in the way that best serves the needs of their facility. It can be used to create functionality that is not specifically available in the standard interface, such as automatic marker detection, exportation of images of non-standard dose planes, and images of all control points can be utilized as desired.
DATA MINING
Clinics get access to data in RayStation using the powerful scripting capabilities and can find any information about single or multiple patients to reduce research times.